Getting Started with MicroMod
Hardware Overview
What Connector and Key Does MicroMod Use?
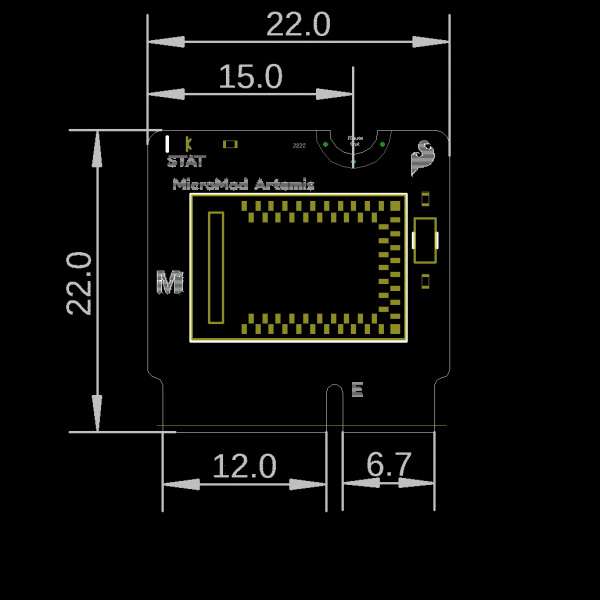
MicroMod uses the common M.2 connector. This is the same connector found on modern motherboards and laptops. We recommend the connector with 4.2mm height.
 |
 |
| M.2 Connector Socket View | M.2 Connector View from Back |
TE makes the 2199230-4 that is widely available and for reasonable cost (1k budgetary pricing is $0.56). You can also order the MicroMod DIY Carrier Kit that includes 5 of the connector, screw, and reflow-able standoff.
There are various locations for the plastic ‘key’ on the M.2 connector to prevent a user from inserting an incompatible device. The MicroMod standard uses the ‘E’ key but diverges from the M.2 standard by moving the mounting screw 4mm to the side. The ‘E’ key is fairly common so a user could insert a M.2 compatible Wifi module but because the screw mount doesn’t align, the user would not be able to secure an incompatible device into a MicroMod carrier board.
What is a Processor Board?
Each processor board is approximately 22x22mm and has a microcontroller or processor on it. The pins on the processor are brought to the card edge to match the MicroMod pinout specification.
Every processor board is expected to need only USB D+/- to be programmed. This means that a processor that does not have built-in USB Support must have it added. For example: the Artemis Processor board has the CH340E added to provide serial programming support.
Every processor board is expected to have one on-board status LED that is not routed to the board edge.
Note: The MicroMod spec moves the screw position from the board's center line to 4mm right-of-center. This is meant to prevent incorrect mixing of a growing number of devices that use the M.2 connector (such as WiFi cards, SSDs, cellular modems, etc) and MicroMod devices. While a user could insert a WiFi card into a SparkFun data logging carrier board the screw holes would not line up making it obvious the devices don't work together.
The MicroMod spec may incorporate larger sizes in the future, and users are welcome to create their own processor boards, but note that the standoff hole on most carrier boards will be located to fit the 2222 MicroMod key.
What is the MicroMod Pinout?
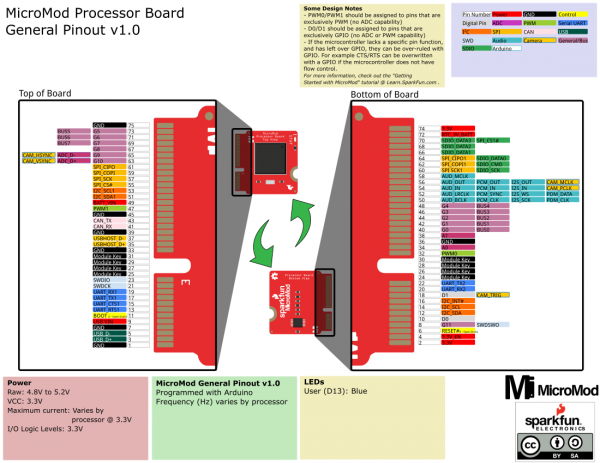
The MicroMod interface is defined as follows:
Note that the M.2 connector pins on opposing sides are offset from each other as indicated by the bottom pins. It's not as apparent in the table further below since it is not offset. As a result, one row for the bottom pins are "Not Connected".
Below is the general MicroMod interface pinout for v1.0 processor and carrier boards.
Not all of the pins are guaranteed to be connected when using the MicroMod form factor. Please see the documentation specific to your processor board for more information.
| AUDIO | UART | GPIO/BUS | I2C | SDIO | SPI | Dedicated |
| Function | Bottom Pin |
Top Pin |
Function | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Not Connected) | 75 | GND | |||||||
| 3.3V | 74 | 73 | G5 / BUS5 | ||||||
| RTC_3V_BATT | 72 | 71 | G6 / BUS6 | ||||||
| SPI_CS1# | SDIO_DATA3 (I/O) | 70 | 69 | G7 / BUS7 | |||||
| SDIO_DATA2 (I/O) | 68 | 67 | G8 | ||||||
| SDIO_DATA1 (I/O) | 66 | 65 | G9 | ADC_D- | CAM_HSYNC | ||||
| SPI_CIPO1 | SDIO_DATA0 (I/O) | 64 | 63 | G10 | ADC_D+ | CAM_VSYNC | |||
| SPI COPI1 | SDIO_CMD (I/O) | 62 | 61 | SPI_CIPO (I) | |||||
| SPI SCK1 | SDIO_SCK (O) | 60 | 59 | SPI_COPI (O) | LED_DAT | ||||
| AUD_MCLK (O) | 58 | 57 | SPI_SCK (O) | LED_CLK | |||||
| CAM_MCLK | PCM_OUT | I2S_OUT | AUD_OUT | 56 | 55 | SPI_CS# | |||
| CAM_PCLK | PCM_IN | I2S_IN | AUD_IN | 54 | 53 | I2C_SCL1 (I/O) | |||
| PDM_DATA | PCM_SYNC | I2S_WS | AUD_LRCLK | 52 | 51 | I2C_SDA1 (I/O) | |||
| PDM_CLK | PCM_CLK | I2S_SCK | AUD_BCLK | 50 | 49 | BATT_VIN / 3 (I - ADC) (0 to 3.3V) | |||
| G4 / BUS4 | 48 | 47 | PWM1 | ||||||
| G3 / BUS3 | 46 | 45 | GND | ||||||
| G2 / BUS2 | 44 | 43 | CAN_TX | ||||||
| G1 / BUS1 | 42 | 41 | CAN_RX | ||||||
| G0 / BUS0 | 40 | 39 | GND | ||||||
| A1 | 38 | 37 | USBHOST_D- | ||||||
| GND | 36 | 35 | USBHOST_D+ | ||||||
| A0 | 34 | 33 | GND | ||||||
| PWM0 | 32 | 31 | Module Key | ||||||
| Module Key | 30 | 29 | Module Key | ||||||
| Module Key | 28 | 27 | Module Key | ||||||
| Module Key | 26 | 25 | Module Key | ||||||
| Module Key | 24 | 23 | SWDIO | ||||||
| UART_TX2 (O) | 22 | 21 | SWDCK | ||||||
| UART_RX2 (I) | 20 | 19 | UART_RX1 (I) | ||||||
| CAM_TRIG | D1 | 18 | 17 | UART_TX1 (0) | |||||
| I2C_INT# | 16 | 15 | UART_CTS1 (I) | ||||||
| I2C_SCL (I/0) | 14 | 13 | UART_RTS1 (O) | ||||||
| I2C_SDA (I/0) | 12 | 11 | BOOT (I - Open Drain) | ||||||
| D0 | 10 | 9 | USB_VIN | ||||||
| SWO | G11 | 8 | 7 | GND | |||||
| RESET# (I - Open Drain) | 6 | 5 | USB_D- | ||||||
| 3.3V_EN | 4 | 3 | USB_D+ | ||||||
| 3.3V | 2 | 1 | GND | ||||||
| Signal Group | Signal | I/O | Description | Voltage | Power | 3.3V | I | 3.3V Source | 3.3V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GND | Return current path | 0V | ||
| USB_VIN | I | USB VIN compliant to USB 2.0 specification. Connect to pins on processor board that require 5V for USB functionality | 4.8-5.2V | |
| RTC_3V_BATT | I | 3V provided by external coin cell or mini battery. Max draw=100μA. Connect to pins maintaining an RTC during power loss. Can be left NC. | 3V | |
| 3.3V_EN | O | Controls the carrier board's main voltage regulator. Voltage above 1V will enable 3.3V power path. | 3.3V | |
| BATT_VIN/3 | I | Carrier board raw voltage over 3. 1/3 resistor divider is implemented on carrier board. Amplify the analog signal as needed for full 0-3.3V range | 3.3V | |
| Reset | Reset | I | Input to processor. Open drain with pullup on processor board. Pulling low resets processor. | 3.3V |
| Boot | I | Input to processor. Open drain with pullup on processor board. Pulling low puts processor into special boot mode. Can be left NC. | 3.3V | |
| USB | USB_D± | I/O | USB Data ±. Differential serial data interface compliant to USB 2.0 specification. If UART is required for programming, USB± must be routed to a USB-to-serial conversion IC on the processor board. | |
| USB Host | USBHOST_D± | I/O | For processors that support USB Host Mode. USB Data±. Differential serial data interface compliant to USB 2.0 specification. Can be left NC. | |
| CAN | CAN_RX | I | CAN Bus receive data. | 3.3V |
| CAN_TX | O | CAN Bus transmit data. | 3.3V | |
| UART | UART_RX1 | I | UART receive data. | 3.3V |
| UART_TX1 | O | UART transmit data. | 3.3V | |
| UART_RTS1 | O | UART ready to send. | 3.3V | |
| UART_CTS1 | I | UART clear to send. | 3.3V | |
| UART_RX2 | I | 2nd UART receive data. | 3.3V | |
| UART_TX2 | O | 2nd UART transmit data. | 3.3V | |
| I2C | I2C_SCL | I/O | I2C clock. Open drain with pullup on carrier board. | 3.3V |
| I2C_SDA | I/O | I2C data. Open drain with pullup on carrier board | 3.3V | |
| I2C_INT# | I | Interrupt notification from carrier board to processor. Open drain with pullup on carrier board. Active LOW | 3.3V | |
| I2C_SCL1 | I/O | 2nd I2C clock. Open drain with pullup on carrier board. | 3.3V | |
| I2C_SDA1 | I/O | 2nd I2C data. Open drain with pullup on carrier board. | 3.3V | |
| SPI | SPI_COPI | O | SPI Controller Output/Peripheral Input. | 3.3V |
| SPI_CIPO | I | SPI Controller Input/Peripheral Output. | 3.3V | |
| SPI_SCK | O | SPI Clock. | 3.3V | |
| SPI_CS# | O | SPI Chip Select. Active LOW. Can be routed to GPIO if hardware CS is unused. | 3.3V | |
| SPI/SDIO | SPI_SCK1/SDIO_CLK | O | 2nd SPI Clock. Secondary use is SDIO Clock. | 3.3V |
| SPI_COPI1/SDIO_CMD | I/O | 2nd SPI Controller Output/Peripheral Input. Secondary use is SDIO command interface. | 3.3V | |
| SPI_CIPO1/SDIO_DATA0 | I/O | 2nd SPI Peripheral Input/Controller Output. Secondary use is SDIO data exchange bit 0. | 3.3V | |
| SDIO_DATA1 | I/O | SDIO data exchange bit 1. | 3.3V | |
| SDIO_DATA2 | I/O | SDIO data exchange bit 2. | 3.3V | |
| SPI_CS1/SDIO_DATA3 | I/O | 2nd SPI Chip Select. Secondary use is SDIO data exchange bit 3. | 3.3V | |
| Audio | AUD_MCLK | O | Audio master clock. | 3.3V |
| AUD_OUT/PCM_OUT/I2S_OUT/CAM_MCLK | O | Audio data output. PCM synchronous data output. I2S serial data out. Camera master clock. | 3.3V | |
| AUD_IN/PCM_IN/I2S_IN/CAM_PCLK | I | Audio data input. PCM syncrhonous data input. I2S serial data in. Camera periphperal clock. | 3.3V | |
| AUD_LRCLK/PCM_SYNC/I2S_WS/PDM_DATA | I/O | Audio left/right clock. PCM syncrhonous data SYNC. I2S word select. PDM data. | 3.3V | |
| AUD_BCLK/PCM_CLK/I2S_CLK/PDM_CLK | O | Audio bit clock. PCM clock. I2S continuous serial clock. PDM clock. | 3.3V | |
| SWD | SWDIO | I/O | Serial Wire Debug I/O. Connect if processor board supports SWD. Can be left NC. | 3.3V |
| SWDCK | I | Serial Wire Debug clock. Connect if processor board supports SWD. Can be left NC. | 3.3V | |
| ADC | A0 | I | Analog to digital converter 0. Amplify the analog signal as needed to enable full 0-3.3V range. | 3.3V |
| A1 | I | Analog to digital converter 1. Amplify the analog signal as needed to enable full 0-3.3V range. | 3.3V | |
| PWM | PWM0 | O | Pulse width modulated output 0. | 3.3V |
| PWM1 | O | Pulse width modulated output 1. | 3.3V | |
| Digital | D0 | I/O | General digital input/output pin. | 3.3V |
| D1/CAM_TRIG | I/O | General digital input/output pin. Camera trigger. | 3.3V | |
| General/Bus | G0/BUS0 | I/O | General purpose pins. Any unused processor pins should be assigned to Gx with ADC + PWM capable pins given priority (0, 1, 2, etc.) positions. The intent is to guarantee PWM, ADC and Digital Pin functionality on respective ADC/PWM/Digital pins. Gx pins do not guarantee ADC/PWM function. Alternative use is pins can support a fast read/write 8-bit or 4-bit wide bus. | 3.3V |
| G1/BUS1 | I/O | 3.3V | ||
| G2/BUS2 | I/O | 3.3V | ||
| G3/BUS3 | I/O | 3.3V | ||
| G4/BUS4 | I/O | 3.3V | ||
| G5/BUS5 | I/O | 3.3V | ||
| G6/BUS6 | I/O | 3.3V | ||
| G7/BUS7 | I/O | 3.3V | ||
| G8 | I/O | General purpose pin | 3.3V | |
| G9/ADC_D-/CAM_HSYNC | I/O | Differential ADC input if available. Camera horizontal sync. | 3.3V | |
| G10/ADC_D+/CAM_VSYNC | I/O | Differential ADC input if available. Camera vertical sync. | 3.3V | |
| G11/SWO | I/O | General purpose pin. Serial Wire Output | 3.3V |
Each pin on the M.2 connector is specified to have a given function. There are additional rules to the MicroMod specification to ensure cross platform compatibility. At the extreme case, a maximum of 49x GPIOs are supported. In general, MicroMod focuses on interface types and locations. For example, if a carrier board requires PWM capabilities then the carrier board should leverage pins 32 (aka PWM0) and 47 (aka PWM1) as these are most likely to support PWM.
Supported Interfaces:
- USB for programming and serial debug
- 2x Analog Dedicated
- 2x PWM Dedicated
- 2x Digital I/O Dedicated
- 12x GPIO
- 2x I2C
- 2x SPI
- 2x UART
- SDIO
- USB-HOST
- CAN
- SWD
- PDM / PCM / I2S
- Differential ADC
12x GPIOs may not sound like much but once all the other interfaces have been connected (UART, SPI, I2C, PWM, ADC) 12x GPIOs should cover most remaining applications.